想了解DW310-35 0.35*1000*C 电机铁芯用钢产品的更多信息?一部视频,让你轻松get到所有重点!
以下是:DW310-35 0.35*1000*C 电机铁芯用钢的图文介绍

电工钢硅钢片Electrical steel, also known as silicon steel sheet, is an indispensable metal material in the power, electronics, and military industries, and is also the largest functional material in production. It is mainly used as the iron core for various motors, generators, and transformers. Since it is a functional material, its performance testing also revolves around "function". These indicators are often mentioned in trade and processing processes, and a brief understanding can help everyone better carry out their work. The performance testing of electrical steel mainly includes the following aspects: magnetic inspection, stacking coefficient inspection, coating adhesion inspection, repeated bending inspection, size and shape surface inspection, and conventional mechanical property inspection. In addition to the types of products listed above, there are also some special purpose electrical steel plates, such as 0.15 and 0.20mm thick 3% Si cold-rolled non oriented silicon steel strips and 0.025, 0.05, and 0.1mm thick 3% Si cold-rolled oriented silicon steel strips, which are used as intermediate and intermediate grade High frequency motors and transformers, as well as pulse transformers, etc; 0.7mm thick 3% Si high-strength cold-rolled non oriented silicon steel plate for relays and power switches; High strength cold-rolled electrical steel plate for new high-speed motor rotors; Low carbon electrical steel hot-rolled thick and cold-rolled plates for magnetic shielding and high-energy accelerator electromagnets such as medical magnetic resonance tomography scanners; 4.5% to 6.5% Si high silicon steel plates for high-frequency motors, transformers, and magnetic shielding.
Generally, motors, transformers, and other electrical components are required to have high efficiency, low power consumption, small size, and light weight. Electrical steel plates are usually guaranteed to have magnetic properties based on core loss and magnetic induction strength. Magnetic induction strength is the number of magnetic lines passing through a unit cross-sectional area of the iron core, also known as magnetic flux density. It represents the material‘s magnetization ability, measured in T. The magnetic induction strength of electrical steel plates is high, and the excitation current (also known as no-load current) of the iron core is reduced. Copper and iron losses are also reduced, which can save electrical energy. When the power of the motor and transformer remains constant, the magnetic induction intensity is high, and the design Bm can be increased. The cross-sectional area of the iron core can be reduced, which reduces the volume and weight of the iron core, and saves the amount of electrical steel plates, wires, insulation materials, and structural materials used. This can reduce the total loss and manufacturing cost of the motor and transformer, and is beneficial for the manufacturing, installation, and transportation of large transformers and motors. The main requirements for the performance of silicon steel are:
1. Low iron loss is the most important indicator of the quality of silicon steel sheets. Various countries classify grades based on iron loss values, with the lower the iron loss, the higher the grade.
2. Under strong magnetic fields, the magnetic induction intensity (magnetic induction) is high, which reduces the volume and weight of the iron core of the motor and transformer, saving silicon steel sheets, copper wires, and insulation materials.
3. The surface is smooth, flat, and the thickness is uniform, which can improve the filling coefficient of the iron core.
4. Good lamination performance is more important for manufacturing micro and small electric motors.
5. The adhesion and weldability of the surface insulation film are good, which can prevent corrosion and improve the punching performan


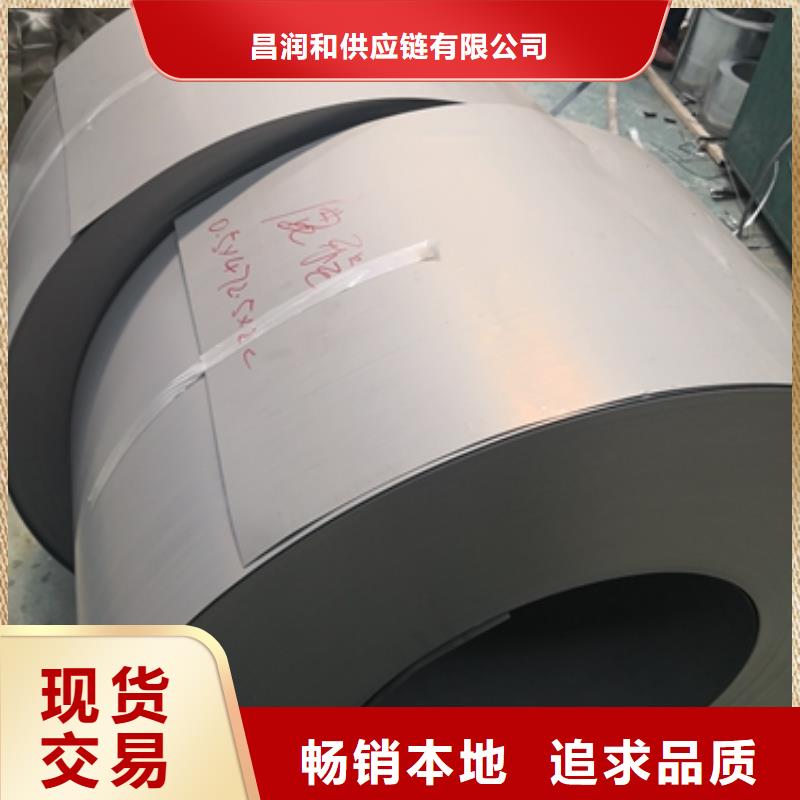
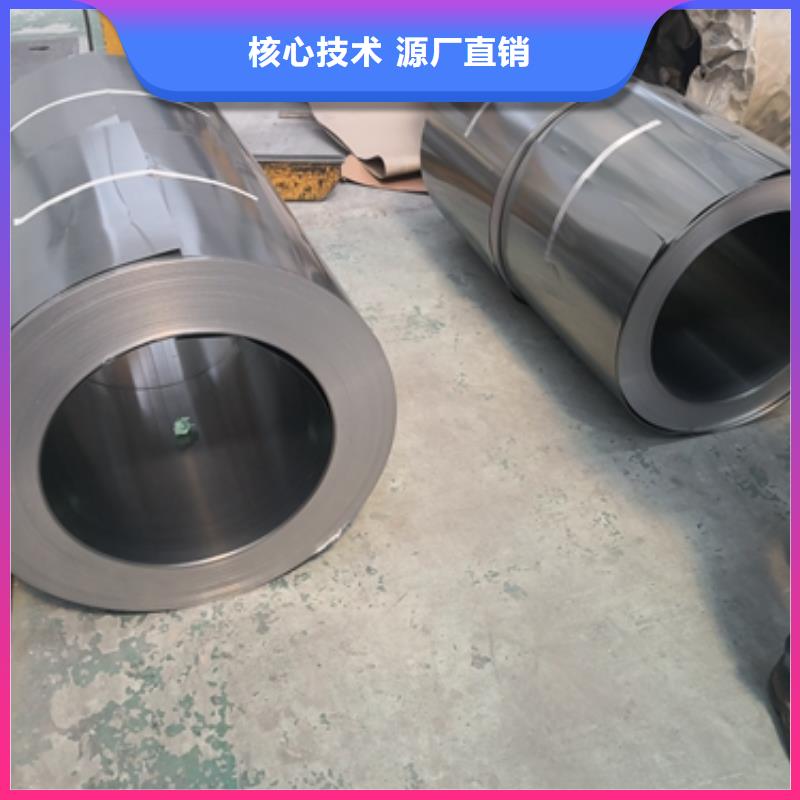
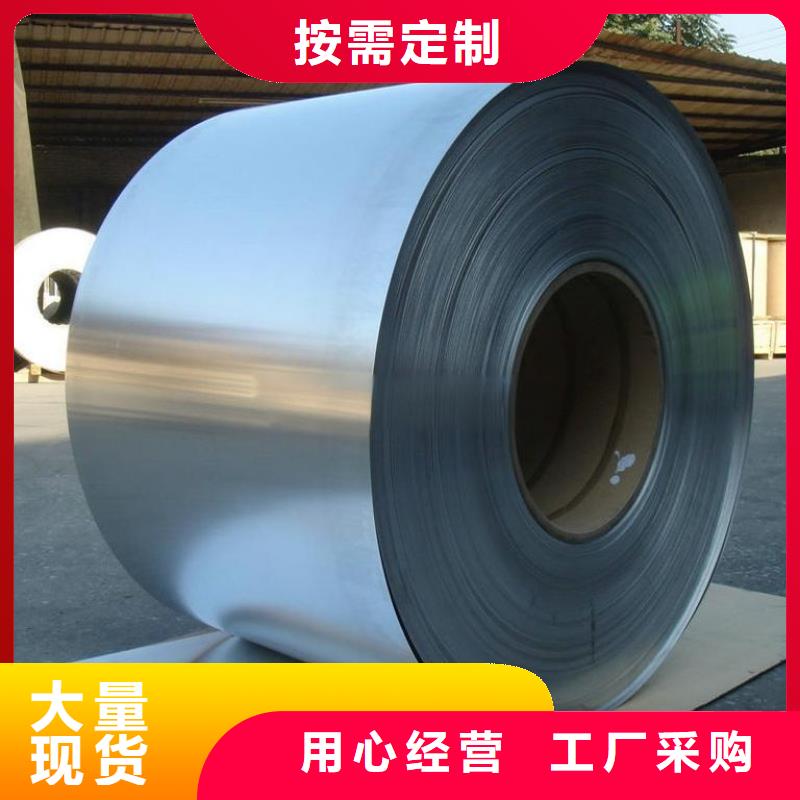
电工钢硅钢片 电工钢板通常是以铁芯损耗和磁感应强度作为产品磁性保证值[1] [2] 。对电工钢板性能的要求如下:铁芯损耗(PT)低铁芯损耗是指铁芯在≥50Hz交变磁场下磁化时所消耗的无效电能,简称铁损,也称交变损耗,其单位为W/kg。这种由于磁通变化受到各种阻碍而消耗的无效电能,通过铁芯发热既损失掉电能,又引起电机和变压器的温升。电工钢的铁损(PT)包括磁滞损耗、云南楚雄本地涡流损耗(Pe)和反常损耗(Pa)三部分。电工钢板铁损低,既可节省大量电能,又可延长电机和变压器工作运转时间,并简化冷却装置。由于电工钢板的铁损所造成的电量损失占各国全年发电量的2.5%~4.5%,因此各国生产电工钢板总是千方百计设法降低铁损,并以铁损作为考核产品磁性的重要指标,按产品的铁损值作为划分产品牌号的依据。冷轧取向电工钢:冷轧取向电工钢是电工钢中的高端产品,与冷轧无取向电工钢相比,磁性具有强烈的方向性;在易磁化的轧制方向上具有优越的高磁导率与低损耗特性。取向钢带在轧制方向的铁损仅为横向的1/3,磁导率之比为6:1。用途:冷轧取向硅钢带主要的用途是用于变压器制造。
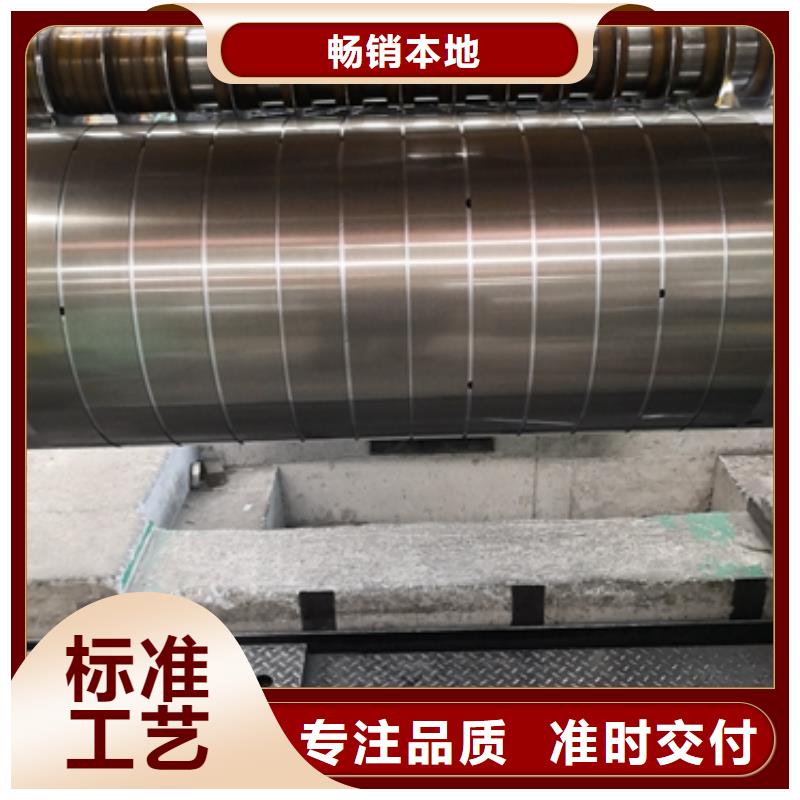


电工钢硅钢片1882~1995年主要是热轧硅钢的发展阶段。1903年美国和德国首先开始生产热轧硅钢。1905年美国(英国在1906年)已经大规模生产,在很短的时间内全部替代了普通低碳钢板制造电机和变压器。由于冷轧无取向硅钢的磁感、云南楚雄当地铁损、云南楚雄当地冲剪加工性、云南楚雄当地表面质量和绝缘涂层等质量性能都大大优于热轧硅钢,并且热轧产品不能成卷生产,降低了冲片效率,60年代主要的工业发达 都陆续停止生产热轧硅钢。1957年,前西德阿什姆斯在实验室内生产出了双取向硅钢片(立方织构的硅钢)。沿轧向和横向都有很高的磁性,但尚在实验室阶段,未投入工业生产。


电工钢硅钢片硅钢是一种硅铁合金。用硅钢轧制的片材是电工领域中应用广的软磁材料,因而硅钢片又称电工钢片。硅钢片广泛用于电动机、发电机、变压器、扼流圈、电磁机构、继电器及测量仪表中电机工业大量使用厚度为0.35~0.50mm的硅钢片,用于:中型旋转机,压缩电机,通用马达,小型精密电机,电动汽车,压缩机,通用电机,电源变压器,精密变压器,节能电机,焊机变压器,稳压器,磁性密封器,加速器用电磁铁,汽车电机等;在电信高频技术中常用0.05~0.20mm的薄带钢片,以便更有效地降低涡流损耗。热轧硅钢片厚度为0.35~0.50mm,密度为7.55~7.70g/cm3,多用于大、中、小型交、直流电动机;冷轧无取向硅钢片厚度为0.35~0.50mm,密度为7.65~7.75g/cm3,多用于大型交流发电机、电动机,大、中、小型交、直流电动机;冷轧取向硅钢片厚度为0.23mm 0.27mm 0.3mm 0.35mm,密度为7.65g/cm3,多用于电力变压器、油浸式变压器,干式变压器,电抗器、磁放大器等;冷轧取向薄带厚度为0.05~0.20mm,多用于无线电高频变压器。


鹿程国际贸易有限公司为您找到优质的 云南楚雄电工钢信息,在这您可以查看 云南楚雄电工钢报价、行情、参数、厂家介绍等,联系人:鹿丙伟,地址:宝山区蕰川公路777号宝钢厂区607-609室